
While eating gluten-free (GF) has become something of a fad, for many, the real reason behind this style of eating is to prevent unwanted symptoms.
The primary reason to cut out gluten-containing foods is for people who suffer from Coeliac Disease and Gluten Intolerance.
How might you feel if you are gluten-sensitive?
Common Symptoms
| Sore Stomach | Bloated Stomach | Lots of gas |
| Feeling Dizzy | Vomiting | Diarrhaea |
| Constipation | Feeling Tired | Weight Loss/gain |
| Mouth Ulcers |
Serious Symptoms
| Thin and weak bones | Diabetes |
| Trouble getting pregnant | Low iron in your blood |
| Depression, feeling sad | Poor teeth and gum disease |
| Cancer |
It has been found that intolerance and sensitivity to gluten, a debilitating digestive condition, is four times more common today than it was in the 1950’s. (Source: World Health)
What is gluten?
Gluten is one of the largest and most complex proteins eaten by man and is found naturally in grass grains, specifically in wheat, barley, and rye.
- Wheat is a grain used as an ingredient in bread, pasta, and cereal. Wheat often appears in foods like soups, salad dressings, and processed foods as well.
- Barley is commonly found in beer and foods containing malt.
- Rye is most often found in rye bread, rye beer, and some cereals.
What is gluten intolerance?
Many people are unaware that there is a difference between Celiac disease and gluten intolerance. Coeliac Disease is an autoimmune disorder that occurs in genetically predisposed people in which the immune system responds abnormally to gluten.
“Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disorder that can occur in genetically predisposed people where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. It is estimated to affect 1 in 100 people worldwide. Two and one-half million Americans are undiagnosed and are at risk for long-term health complications.” (Celiac Disease Foundation)
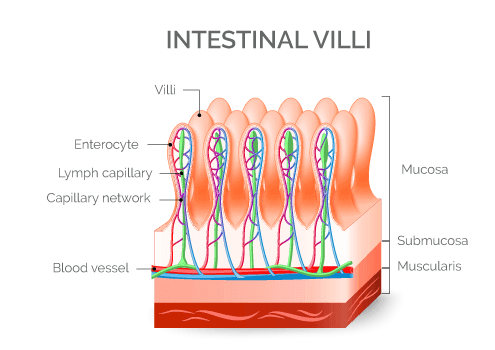
When people with Celiac disease eat gluten-containing foods, their body mounts an immune response that attacks the small intestine. These attacks lead to damage of the villi, small finger-like projections that line the small intestine, that promote nutrient absorption. And when the villi get damaged, nutrients cannot be absorbed properly into the body.
Gluten sensitivity (intolerance) on the other hand, is not an autoimmune disorder, and describes a set of symptoms that people attribute to dietary gluten.
Both gluten sensitivity and Celiac disease and the inability to digest gluten, may lead to the person experiencing any number of symptoms. The challenging part is that each person may experience a different set of symptoms and less than 30% of sufferers have any digestive symptoms at all.
Gluten intolerance symptoms
Digestive Symptoms |
Skin Symptoms |
Mental Symptoms |
Body Symptoms |
Autoimmune diseases |
| Bloating | Keratosis Pilaris | Mental Fatigue | Joint Pain | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Gas | Hives | Neurological issues | Heartburn | Lupus |
| Diarrhea | Rash | Depression | Dental problems | Multiple Sclerosis |
| Constipation | Eczema | Anxiety | Mouth Ulcers | Cancer |
| Nausea | Psoriasis | Irritability | Unexplained weight loss or gain | Hashimoto Thyroiditis |
| Vomiting | Lack of attention span | Hormone imbalance | Graves Disease | |
| Mood swings | Migraines | Chron’s | ||
| Infertility | Ulcerative Colitis | |||
| Chronic fatigue | Dermatitis | |||
| Osteoporosis | Herpetiformis | |||
| Nutrition malabsorption |
Gluten intolerance diagnosis
It takes a skilled practitioner to carefully analyse your given set of symptoms and the systems of your body to determine if you may have Celiac disease or food sensitivities.
There is a range of tests that allow for an accurate diagnosis. This may include blood testing to measure the level of antibodies to gluten, gene testing in relation to the genes associated with Celiac disease, investigations to see if the lining of the small intestine (micro-villi) have been damaged, and/or food elimination diets.
It’s true you can skip the diagnosis and just stop eating Gluten, however, in almost every case this step is one of only many that are needed to restore full gut health and regain vibrant energy.
A Gluten-Free Diet
 Talk to our Holistic Healing Practitioner about the appropriate diet to tackle your gluten intolerance. When converting to a gluten-free diet, common symptoms that may occur due to withdrawal or detoxification from gluten include:
Talk to our Holistic Healing Practitioner about the appropriate diet to tackle your gluten intolerance. When converting to a gluten-free diet, common symptoms that may occur due to withdrawal or detoxification from gluten include:
- Food craving
- Disorientation
- Irritability
- Sleepiness
- Depression
- Mental fogginess
- Shortness of breath
Our Holistic Healing Practitioners have helped hundreds of people to switch to a gluten-free diet and can help you to move through these withdrawal symptoms quickly. We have more than one trick up our sleeve to make this process more enjoyable.
Contact us today at (08) 9388 2768, quote this article and receive a complimentary 10-minute phone consultation.
At Effortless Superhuman, we take a holistic approach to healthcare and believe the body can heal itself from disease, pain, and injury, as long as the barriers to healing are removed.
